Emergence, key components and potential impact of a revolutionary phenomenon
In the ever-changing world of the Internet of Things (IoT), a brand-new technological revolution is currently taking shape: the Spatial Web. Whilst IoT has already transformed the way we interact with different devices, the Spatial Web takes things further by creating an immersive experience that rethinks the line between the physical and the virtual world. This revolutionary phenomenon promises to redefine connectivity, paving the way to new prospects for tech companies. In this article, we will explore the emergence of the Spatial Web, its key components and its potential impact on corporate R&D.
In comparison to Web 2.0 which we all know and use virtually on a daily basis, Web 3.0 has four different features:
- The presence of a web focused more on semantics and that can take advantage of AI to understand what a user or a customer may be trying to say, or intends to do. This research algorithm is designed to provide more accurate understanding of searches based on the genuine meaning of search words rather than key words or figures.
- The capacity to browse using virtual reality (VR) headsets that immerse the user in what is, by nature, a more realistic environment.
- The key behind Web 3.0 is the use of the blockchain and of cryptocurrencies, which theoretically enables us to bypass intermediaries, hence facilitating direct interparty transactions.
- Finally, Web 3.0 applications are characterised by a constant high-speed 5G, Wi-Fi or IoT connection.
In contrast, if we speak generally about Web 3.0 from the user’s viewpoint, the other - more generic - term for the same technology, i.e. the SPATIAL WEB, encompasses a largely more industrial normative and applicative dimension.
Changing the IoT as we know it
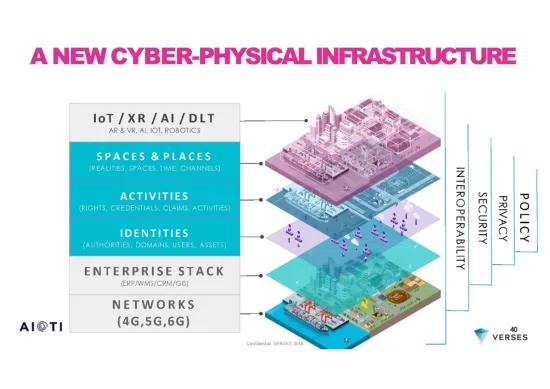
The Spatial Web, also known as Spatial Internet, will enable silos of data patiently built over the years to be opened up. The SPATIAL WEB will enable each feature of the physical world to interact with the digital world and vice versa. This natural evolution of the IoT aims at integrating artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to create an interactive and collaborative environment. In contrast with traditional IoT, in which devices are connected via physical networks, the Spatial Web will break down barriers by allowing objects and users to co-exist in a 3-dimensional digital world.
Vast opportunities
The emergence of the Spatial Web offers a host of opportunities for R&D managers of tech companies. Here are a few examples of fields that can yield significant benefit from the Spatial Web:
- Advanced user experience: The Spatial Web paves the way to a highly personalised and interactive experience for the user. Businesses can develop innovative applications that engage customers in a totally novel manner, hence stimulating their interest and reinforcing their brand loyalty.
- Groundbreaking industrial solutions: In the industrial sector, the Spatial Web can improve operational efficiency and safety. Virtual reality simulations can be used to train employees on complex tasks, hence reducing risks and the costs associated with traditional training approaches.
- New commercial opportunities: The Spatial Web opens new markets and brings new commercial opportunities. Businesses can create innovative products and services, such as virtual meeting spaces, on-line art exhibitions or augmented reality tours for tourist attractions.
- Reinforced safety and confidentiality: Whilst the Spatial Web offers a number of advantages, it also brings safety and confidentiality-related challenges. Businesses will need to concentrate on developing robust solutions to protect personal data and to prevent cyberattacks.
Conclusion
The emergence of the Spatial Web promises to radically transform the way we interact with connected devices and digital information. By integrating geospatialisation, augmented reality, virtual reality and artificial intelligence, the Spatial Web will bring new prospects for tech companies, stimulating innovation, creativeness and competitiveness on the global market. R&D managers must seize this opportunity to explore the possibilities offered by the Spatial Web, whilst developing solutions in line with the changing needs of tomorrow’s connected society.